Automate LLM testing in GitHub Actions: secure API keys, organize datasets, run Latitude evaluations, and fail builds on regressions.

César Miguelañez

Jan 14, 2026
Automating large language model (LLM) testing in GitHub Actions ensures consistent quality for AI-powered features. Unlike traditional software, LLMs generate variable outputs, making automated evaluations crucial to detect issues like incorrect tone, fabricated information, or reduced accuracy. Here's the process summarized:
Why Automate Testing: Prevent silent regressions, save time, and use measurable metrics like accuracy and fluency for decision-making.
GitHub Actions Role: Automate evaluations by running tests on every code push or pull request. Fail builds if quality drops below thresholds.
Latitude Integration: Use Latitude, an open-source platform, for prompt management, batch regression testing, and live production monitoring.
Setup Steps:
Secure API Keys: Store credentials safely using GitHub Secrets.
Organize Test Data: Create datasets with inputs and expected outputs for accurate evaluations.
Install Dependencies: Use Latitude CLI or SDKs for Python/TypeScript to manage prompts and run tests.
Create Workflows: Configure GitHub Actions to run tests using Latitude, set pass/fail criteria, and analyze results.
Automated workflows catch issues early, reduce manual validation, and maintain high-quality AI features.
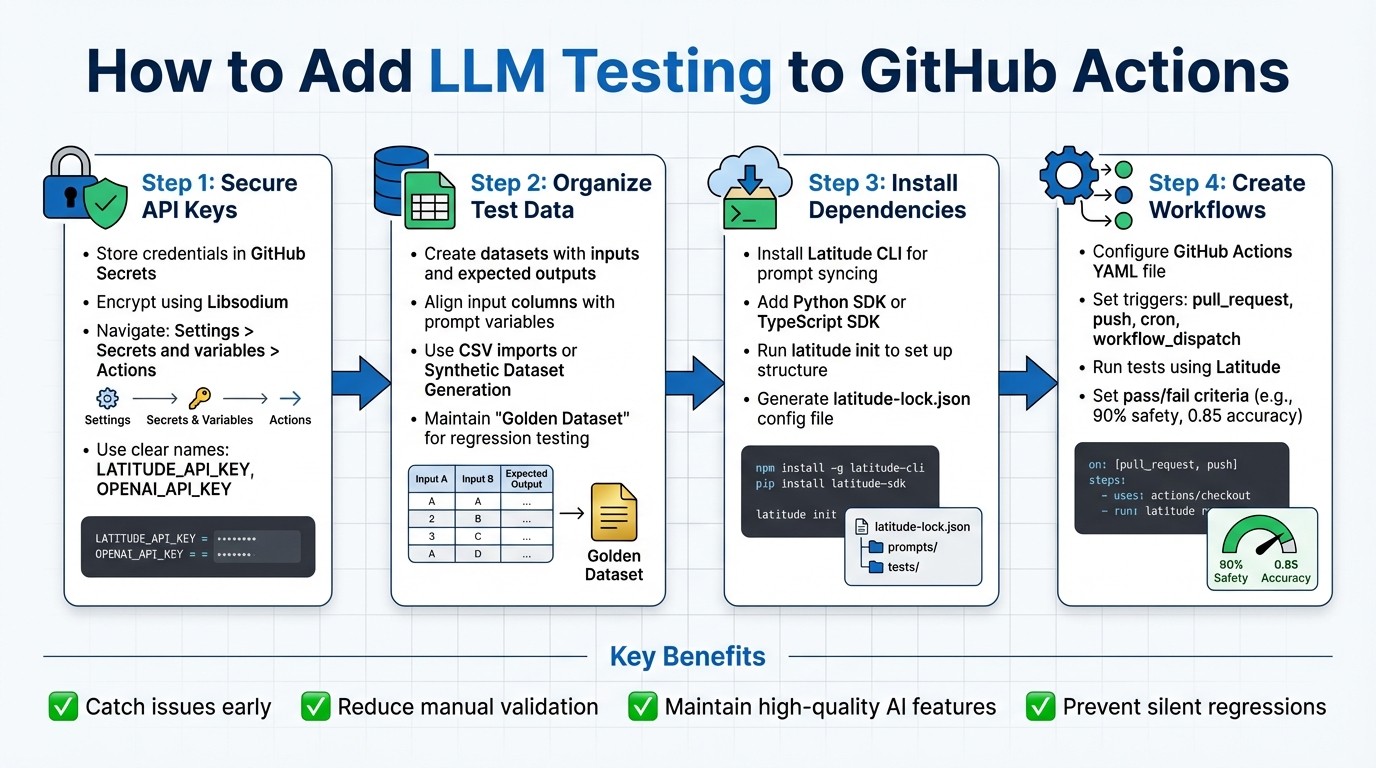
4-Step Process for Adding LLM Testing to GitHub Actions
Preparing Your GitHub Repository for LLM Testing
Getting your GitHub repository ready for LLM testing involves securing credentials, organizing test data, and setting up the necessary tools. These steps help ensure smooth workflows without risking sensitive information or running into missing dependencies.
Storing API Keys and Credentials Securely
Protecting sensitive credentials should be your first priority. GitHub Secrets offers a secure way to store information like LLM API keys or Latitude credentials. These secrets are encrypted using Libsodium and are automatically hidden from logs.
To add a secret, go to Settings > Secrets and variables > Actions > New repository secret. Use a clear name, such as LATITUDE_API_KEY or OPENAI_API_KEY, paste the value, and click Add secret.
If your credentials exceed 48 KB, encrypt them locally using GPG, commit the encrypted file to your repository, and store the decryption passphrase as a secret. For binary files like certificates, encode them in Base64 before storage. You can decode these in your workflow with echo $SECRET | base64 --decode. To manage different environments like development, staging, and production, use environment-level secrets.
Managing Test Data in Latitude
Organizing your test data is essential for effective evaluations. In Latitude, a Dataset is a collection of inputs designed for batch evaluations in regression testing. Make sure the dataset’s input columns align with your prompt variables, and include an expected_output column if needed.
You can create datasets by importing CSV files or using Latitude's Synthetic Dataset Generation tool, which can expand a few examples into thousands of test cases automatically. Keep your datasets organized by purpose - use a "Golden Dataset" for general regression testing and create separate datasets for edge cases or specific scenarios. This approach allows for more targeted evaluations when updating prompts or switching models.
Installing Required Dependencies
Finally, install the tools you’ll need to execute your tests. Start with the Latitude CLI for syncing prompts and managing versions. If your repository uses programmatic integration, install the Python SDK or TypeScript SDK, depending on your project’s language. For TypeScript projects, ensure you have Node.js and npm installed. Python workflows, on the other hand, require a Python environment.
Run latitude init in your repository to set up the directory structure and generate the latitude-lock.json configuration file, which stores your project ID and versioning details. For npm projects, prompts are saved as .js files with default exports. Non-npm projects use .promptl files. Make sure your LATITUDE_API_KEY is accessible as an environment variable in your workflow by pulling it from GitHub Secrets. This ensures smooth authentication for CLI commands and SDK calls.
Creating a GitHub Actions Workflow for LLM Testing
Once your repository is ready, the next step is to set up a GitHub Actions workflow to automatically test your LLM (Large Language Model) features. This involves creating a YAML workflow file that handles evaluations, runs tests using Latitude, and reports the results directly within your GitHub environment.
Setting Up Workflow Triggers
The first thing to configure is when your tests should run. Use pull_request triggers to ensure prompt changes are validated before merging. Additionally, you can set up push events to get instant feedback on every commit.
For more extensive testing, such as evaluating large datasets or experimenting with new prompts, scheduled triggers (using cron syntax) and workflow_dispatch (manual runs) are great options. For instance, you could schedule thorough tests to run daily at 2:00 AM during off-peak hours or allow developers to manually trigger tests for new model versions.
To make testing more efficient, apply path filters to run tests only when specific files change. For example, you can configure the workflow to trigger only when files in your prompts/ directory are modified. Once you've defined these triggers, move on to setting up the steps for executing the tests.
Adding Test Execution Steps
Start by specifying the execution environment with runs-on: ubuntu-latest. Then, include a checkout step to pull your repository's code. If your project uses the Latitude SDK with TypeScript, set up the Node.js runtime. Install dependencies using npm install or the appropriate command for your package manager.
Next, securely load your LATITUDE_API_KEY and provider credentials from GitHub Secrets as environment variables. This ensures sensitive data stays protected. Finally, execute your test script - this could involve running a custom evaluation file or directly invoking Latitude CLI commands.
Running LLM Evaluations with Latitude
With dependencies installed and authentication in place, you can start running evaluations using Latitude. For regression testing, Latitude's Batch Mode is ideal, as it allows you to test against golden datasets. Alternatively, Live Mode can be used to monitor production logs in real time.
Latitude's SDK provides methods to execute prompts and evaluate outputs against predefined quality metrics like accuracy, helpfulness, conciseness, and safety. Set clear pass/fail criteria to maintain high standards. For example, you might require a 90% success rate on safety checks or an accuracy score of at least 0.85.
Once the evaluations finish, Latitude generates aggregated statistics and score distributions. Your workflow can parse these results to decide whether the GitHub Actions job passes or fails. This automated quality check ensures that problematic prompt changes are caught before they reach production.
Reviewing and Acting on Test Results
Once your workflow is complete, it’s time to dive into the evaluation data. How you interpret and act on these results can make all the difference between delivering reliable LLM features and facing quality headaches in production.
Viewing Test Reports in GitHub
To access your evaluation artifacts - like HTML reports, JSON datasets, or CSV files - head to the Actions tab in your GitHub repository. Select the completed workflow run, then scroll down to the Artifacts section. For quick insights, you can configure your workflow to display key metrics directly in the run summary. Using GitHub’s job annotations, you can instantly view pass/fail statuses, composite scores, and critical failures without needing to download files.
If you're working with Latitude, you can explore results at multiple levels. Individual log entries provide scores for single runs, the Evaluations Tab aggregates statistics and shows time-series trends, and the Experiments tab lets you compare prompt variants side by side. These tools make it easier to track performance over time and identify areas for improvement.
Tracking Metrics Over Time
Looking at how your LLM features perform across multiple test runs can reveal trends that a single evaluation might not show. Key metrics to monitor include:
Similarity: Measures how closely outputs match reference answers.
Relevance: Assesses whether responses meet user intent.
Groundedness: Evaluates accuracy and avoids hallucinations.
Each metric uses a 0 to 1 scale, with higher scores indicating better performance.
Operational metrics are just as important. Keep an eye on Input Tokens, Output Tokens, and Latency to ensure your model stays efficient and responsive. For example, in a June 2025 evaluation, GPT-4.1 achieved 100% Similarity with a latency of 918ms, while DeepSeek-R1 only reached 50% Similarity with a much slower latency of 2,285ms. This comparison underscores how model choice can directly impact both quality and speed.
For negative metrics like toxicity or hallucination detection, lower scores are better. Latitude allows you to optimize for these metrics by setting thresholds - such as requiring correctness above 0.9 or toxicity below 0.1 - to block regressions before they hit production.
Fixing Failed Tests
When tests fail, logs are your best friend. They help you identify where responses fell short and uncover patterns. For example, if Similarity scores are low but Relevance is high, your model might be including unnecessary internal reasoning or "thinking blocks" that deviate from the expected format. In the June 2025 GitHub Models evaluation, DeepSeek-R1 failed a "Dark Mode Request" test with 0% Relevance because it added verbose internal commentary that wasn’t part of the desired output.
Break down failures into two categories:
Objective issues: Problems like incorrect JSON formatting or missing keywords. These can often be fixed by refining prompt instructions or adding programmatic validation rules.
Subjective issues: Challenges like tone or helpfulness. For these, tweak model parameters. For example:
Lower Temperature to 0.2–0.4 for more focused outputs.
Adjust Max Tokens to reduce verbosity.
Apply a Frequency Penalty (0.3–0.5) to cut down on repetitive phrasing.
Latitude's Prompt Suggestions feature can also provide automated guidance based on your evaluation data. Regularly update your golden dataset by including failed test cases or successful edge cases from production. This practice helps prevent regressions and ensures your model continues to improve over time. Latitude’s feedback loop is a valuable tool for refining prompts and maintaining consistent quality.
Conclusion and Next Steps
Automating LLM testing within GitHub Actions takes the place of manual checks, ensuring that silent regressions don’t slip through the cracks. By integrating this step, you can unify your testing process and rely on consistent performance metrics. Instead of relying on manual reviews, automated tests catch potential issues early, guaranteeing that new prompt versions won’t negatively impact performance on tricky edge cases.
Why Automated LLM Testing Matters
The benefits go beyond simply spotting bugs. Automated testing allows for quicker iterations, letting you test and compare different prompt variations in just minutes. Plus, with continuous monitoring, you can pair batch evaluations in CI/CD pipelines with live production tracking. This ensures you can detect regressions caused by model updates or unexpected user behavior. By introducing measurable quality gates, this method shifts evaluations from subjective opinions to decisions backed by solid data.
How to Start with Latitude
Ready to see the benefits for yourself? Here’s how to bring Latitude into your workflow. Use Latitude as an AI Gateway for automated logging, or take full control with the Python or TypeScript SDKs. Start by running latitude login to save your API key, then link your local repository to a Latitude project with latitude init. From there, create a golden dataset with key inputs and expected outputs, set your evaluation criteria (whether using LLM-as-judge or programmatic rules), and enable "Live Evaluation" to monitor quality in real time.
"Tuning prompts used to be slow and full of trial-and-error… until we found Latitude. Now we test, compare, and improve variations in minutes with clear metrics and recommendations."
– Pablo Tonutti, Founder of JobWinner
Latitude offers a free tier so you can explore its features, with paid plans available depending on your usage and integrations. Covering every stage - Design, Test, Deploy, Monitor, Evaluate, and Improve - Latitude equips you with the tools you need to confidently deliver reliable LLM features.
FAQs
How can I use Latitude to streamline LLM testing with GitHub Actions?
Latitude makes it easy to incorporate LLM testing into your GitHub Actions workflow. Here’s how it works:
First, set up an evaluation suite in Latitude. This is where you’ll define your prompts, expected outputs, and the pass/fail thresholds for your tests. Once that’s ready, securely store your Latitude API token in your repository’s GitHub Secrets.
Next, in your workflow, install the Latitude CLI. Use the CLI to run evaluations directly from GitHub Actions. It will test your model, generate a JSON report, and you can configure the workflow to fail if any test doesn’t meet its threshold. Latitude also offers triggers to automatically re-run tests whenever prompts are updated, keeping your evaluations up to date.
After each test run, dive into the Latitude dashboard to review detailed evaluation reports. You can track metrics, spot trends, and address any failing cases. This integration ensures your LLM features stay aligned with your CI/CD pipeline, maintaining consistent quality and performance.
What are the best practices for keeping API keys secure in GitHub Actions?
To keep your API keys safe when using GitHub Actions, here are some key practices to follow:
Use encrypted secrets: Always add API keys as secrets within your repository, environment, or organization settings. Avoid hard-coding them directly into your workflow files.
Apply minimal permissions: Stick to the principle of least privilege. Only grant the necessary access to the
GITHUB_TOKENor any other credentials.Control access: Ensure only users with write access to the repository can view or use secrets. For organization-level secrets, apply strict access policies.
Avoid exposing sensitive data: Never log secrets in workflow logs or error messages to prevent accidental leaks.
Regularly update keys: Rotate API keys periodically, especially if they’ve been regenerated or compromised. Remove any outdated keys immediately.
For those using Latitude for LLM feature development, make sure to store its API keys as GitHub secrets. Reference these keys in your workflows to keep them encrypted, secure, and accessible only to authorized processes.
How can I improve LLM performance metrics with Latitude and GitHub Actions?
To get the most out of Latitude when optimizing LLM performance metrics, start by clearly defining your evaluation criteria. Then, take advantage of Latitude’s built-in tools to test model outputs against expected results. Key metrics like accuracy, relevance, and latency can be measured and stored in an organized format, making analysis straightforward. By version-controlling your prompts and configurations, you can track changes, pinpoint improvements, and easily revert if necessary.
Once your evaluation framework is in place, connect it to GitHub Actions to automatically run tests with every code push or pull request. Latitude’s CLI or API can handle evaluations, with results published as artifacts or displayed on a dashboard for trend tracking. This setup helps you monitor performance metrics over time and establish thresholds to flag regressions before they become issues.
For ongoing monitoring, Latitude offers agents and triggers that can schedule periodic tests or run evaluations only when specific files are updated. This approach helps you identify performance drift while keeping compute costs under control. By combining automated tests, version-controlled assets, and continuous integration feedback, you can systematically fine-tune and enhance your LLM’s performance throughout the development process.